How to Know if You Have Sleep Apnoea
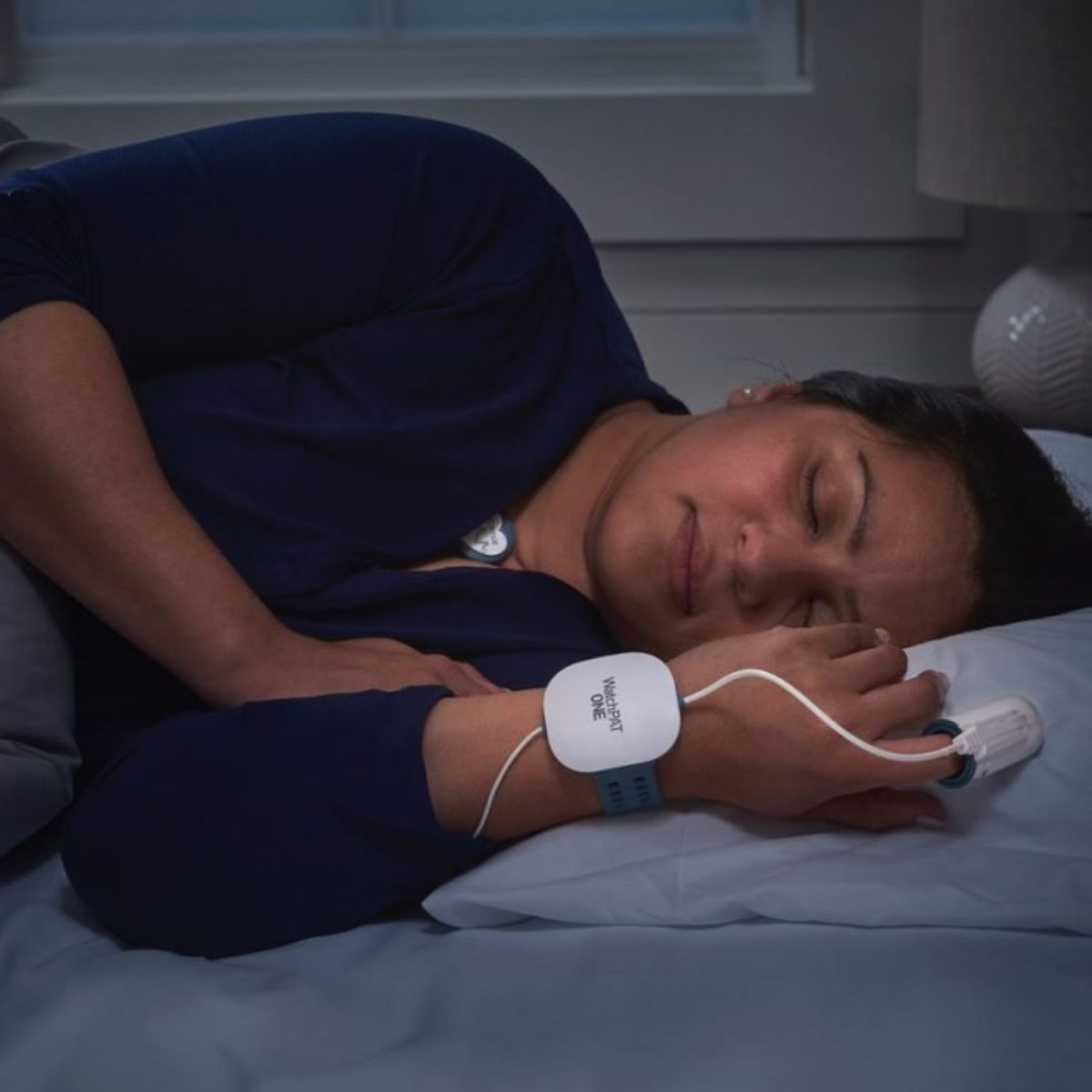

1. Identify the Symptoms of Sleep Apnoea
The first step of diagnosing Sleep Apnoea is to identify the symptoms:
2. Get a Sleep Apnoea Diagnosis
The second step of diagnosing Sleep Apnoea is to confirm your diagnosis with a sleep test. Our home sleep test is a quick and affordable way to confirm Obstructive Sleep Apnoea from the comfort of your home.
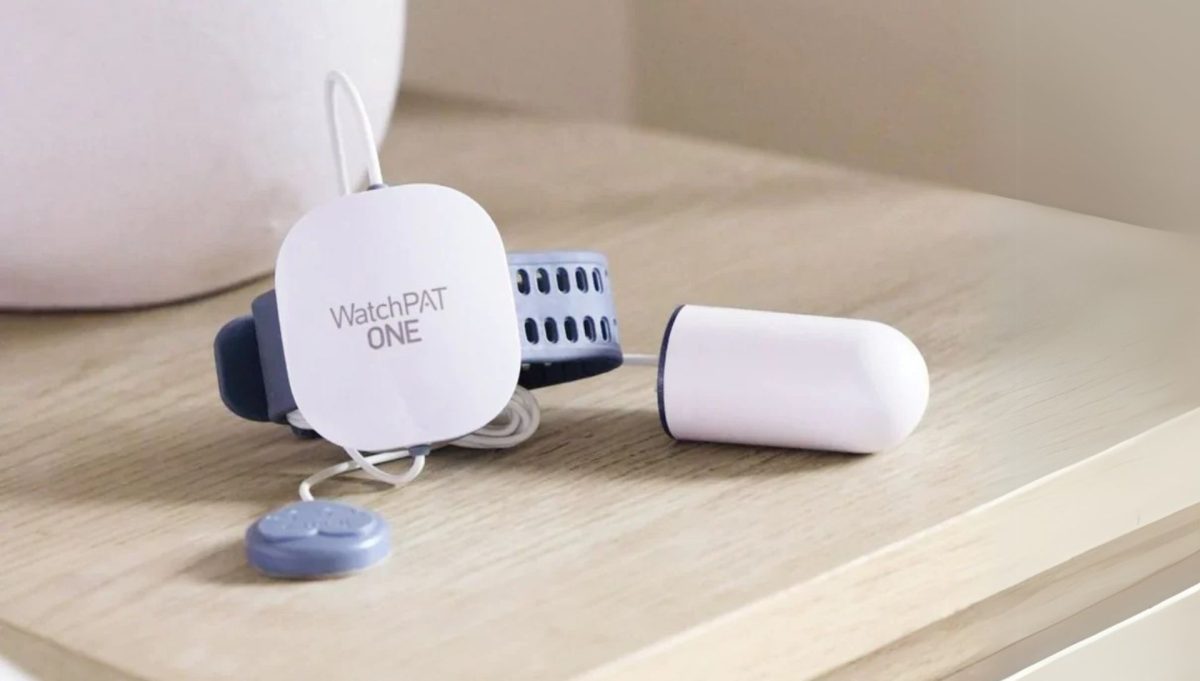

Why Choose a Home Sleep Test?
- Free UK delivery.
- Results in two working days.
- Comparable test results to tests done at a sleep clinic.
- Simple to use at your convenience.
- Follow-up clinical consultation included if diagnosed.
- Confidential – we do not inform the DVLA unless you request it.
3. Start Treatment
Once Sleep Apnoea is diagnosed treatment can start. There are various treatment options that are dependent on the type and severity of a persons Sleep Apnoea.
Among the different options, CPAP therapy is the most widely used and suitable for most people due to its high success rate. For added ease, we offer a unique CPAP Therapy Subscription Service called Intus Plus. The service provides CPAP equipment, clinical consultations, and more for just £49 per month.



